DI Dr. techn. Mugdim Bublin

Favoritenstraße 226, B.3.14
1100 Wien
+43 1 606 68 77-2133
mugdim.bublin@fh-campuswien.ac.at
Education
1993 – 1997: Electrical Engineering TU Vienna
1998 -2014: PhD TU Vienna
Professional Experience
1998 – 2012: Siemens AG
2012 – 2016: Siemens CVC
2016 – 2018: WS Technology GmbH
2018 – 2019: Bosch AG
2009 – 2020: Guest Lecturer FH Kärnten, Klagenfurt
Since November 2019: Teaching and research at FH Campus Vienna, Computer Science and Digital Communications
Since February 2021: Artificial Intelligence Stiftungsprofessor der Stadt Wien
Lectures
Deep Learning and Virtual Reality (Master)
Virtual and Augmented Reality (Bachelor)
Introduction to AI (Bachelor)
Publications
Book Contributions
H. Xiaoben, M. Bublin, J. Hämäläinen and R. Jäntti: ”Self-organized and Bio-inspired Radio Resource Management for WiMAX” Chapter 6 in the book: E. Vivier and G. Vivier (Editors): “Radio Resources Management in Wimax: From Theoretical Capacity to System Simulations”, Wiley, April 2009.
Journal publications
M. Bublin, M. Konegger, P. Slanina: “A Cost Function based Dynamic Channel Allocation and its Limits”, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol. 56, Issue 4, Part 2, pp. 2286-2295, July 2007.
M. Bublin, S. Causevic: “Spectrum and Infrastructure Sharing in Wireless Mobile Networks: Advantages and Risks”, Promet, Traffic&Transportation, Zagreb, Croatia, Vol.20, Issue 4, pp. 221-225, July 2008.
M. Bublin: „Event Detection for Distributed Acoustic Sensing: Combining Knowledge-Based, Classical Machine Learning, and Deep Learning Approaches.“ Sensors 21.22 (2021): 7527.
Reviewed conference papers
M. Bublin, G. Diernhofer, C. F. Mecklenbräuker, T. Pacic, J. Plogsties, P. Slanina: “Simulation of smart antennas in 3G mobile systems”, Proceedings 4th European Personal Mobile Communications Conference EPMCC 2001, Vienna, Feb. 2001.
M. Bublin, G. Ostermayer: “Comparison of Interference Based Dynamic Channel Allocation Algorithms in mobile Networks”, in Proc. of the IEEE SoftCOM’03, Split-Rijeka-Trieste-Venice, Croatia-Croatia-Italy-Italy, Oct. 2003.
M. Bublin, D. Bosanska,O. Hlinka, P. Slanina: “A Self-Adaptive, Utility-based Scheduling for Wireless Cellular Networks”, 16th Mobile and Wireless Summit; Budapest, Hungary, 1. – 7. July 2007.
M. Bublin, I. Kambourov, D. Bosanska, O. Hlinka, O. Hrdlicka, P. Svac, P. Slanina: “Inter-cell Interference Management by Dynamic Channel Allocation, Scheduling and Smart Antennas”, 16th Mobile and Wireless Summit; Budapest, Hungary, 1. – 7. July 2007.
M. Bublin, J. Pan, I. Kambourov, P. Slanina: ”Distributed Spectrum Sharing by Reinforcement and Game Theory”, accepted, 5th Karlsruhe Workshop on Software Radios, 5. – 6. March 2008.
J. Pan, P. Slanina, T. Renk, M. Bublin, I. Kambourov,: ”A cognitive pilot channel system design approach”, 5th Karlsruhe Workshop on Software Radios, 5. – 6. March 2008.
Bublin, M., Schefer-Wenzl, S., Miladinovic I.: “Educating AI Software Engineers: Challenges and Opportunities” in Proceedings of the 24rd International Conference on Interactive Collaborative Learning (ICL2021), Springer International Publishing, 2021.
Klamert Victor, Schmid-Kietreibera Matthias, Bublin Mugdim. “A deep learning approach for real time process monitoring and curling defect detection in selective laser sintering by infrared thermography and convolutional neural networks”, accepted for publication in 12th CIRP Conference on Photonic Technologies [LANE 2022], 4-8 September 2022, Fürth, Germany.
Invited conference presentations
M. Bublin, I. Kambourov: “WINNER – Wireless World Initiative New Radio”, SympoTIC’06, Bratislava, Slovakia, 24. – 27. June 2006.
M. Bublin, G. Mange, M. Olsson, J.P. Javaudin: “WINNER II Inter-cell interference mitigation techniques”, PIMRC, Athens, Greece, 3. – 7. September 2007.
Other publications:
M. Bublin: “Machine Learning for Distributed Acoustic Sensors, Classic versus Image and Deep Neural Networks Approach”, https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.11546, posted on 25.04.2019.
Patents
C. Ball, M. Bublin, M. Garcia-Larrode, K. Ivanov, R. Muellner, G. Ostermayer, P. Slanina, T. Stark: “Dynamic channel allocation for mobile systems”, Filling date 09.07.2002, granted in Germany.
M. Bublin, P. Slanina: “A method and a system for adaptation of a modulation and coding scheme”, EP filling date 21.03.2007.
V. Breuer, M. Bublin, R. Halfmann, P. Slanina, W. Zirwas: “Method and apparatus for transmitting measurement reports in a radio communication system” EP filling date 24.10.2007.
P. Slanina, M. Bublin, I. Kambourov: “Method for time synchronisation in a radio communication system”, EP filling date 25.10.2012, granted 18.05.2016.
P. Slanina, M. Bublin, R. Kronlachner: “Method for suppressing a radio transmission in a cellular radio networ ”, EP filling date 19.03.2013.
P. Slanina, M. Bublin, I. Kambourov: “Method for Doppler frequency offset correction in a cellular radio communication system with a base station and a mobile unit on board of a vehicle moving with high velocity, in particular an aircraft”, EP filling date 19.09.2012, granted 27.04.2016.
P. Slanina, M. Bublin: “Method for determining position of moving object i.e. persons, in inner area environment e.g. tunnel, involves assigning signal sources to distribution assemblies, and deriving position of object from combination of values and signal”, DE filling date 09.08.2012.
M. Bublin: “A Method and Systems for Determining Event Parameters of an Object”, EP filling date 09.01.2017.
PhD Thesis
M. Bublin: “A Pricing and Game Theory based Approach to Radio Resource Management”, TU Vienna, November 2004. http://media.obvsg.at/AC04377590-2001
Diploma Thesis
M. Bublin: “VHDL-Implementierung eines GSM-Kanalcodecs”, TU Vienna, December 1997
Interests
Artificial Intelligence, Machine/Deep Learning, Virtual and Augmented Reality, Robotics, Human-Robot Collaboration
/
Lectures
- Introduction to AI and Data Science (3rd semester bachelor CSDC, compulsory subject)
- Introduction to AI and Data Science (4th semester bachelor CSDC, selected subject)
- Advanced AI and Deep Learning (5th semester bachelor CSDC, selected subject)
- Deep Learning and Virtual Reality (3rd semester master SDE, selected subject)
/
Projects enabled by MA 23:
FH-Call 29: “Stiftungsprofessur – Artificial Intelligence”
FH – Call 30: „AI & VR Lab“
/
Quality Control for Selective Laser Sinterning by Deep Learning
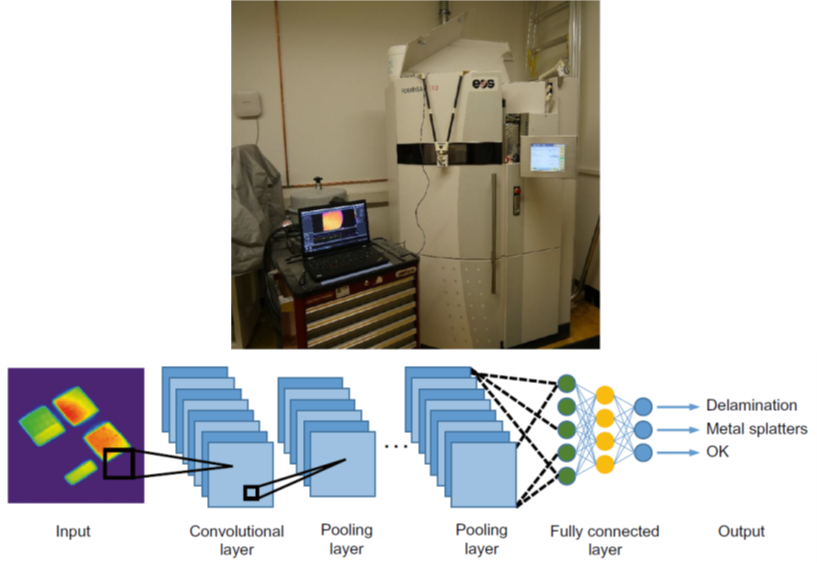
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) of polyamide powders is one of the most prevalent additive manufacturing (AM) processes. Failures induced by curling and other process irregularities affect mechanical properties and part quality. In order to improve cost- and resource-efficiency, flexibility and sustainability of SLS, a real time and in-situ quality control of the whole SLS process chain is needed. Machine learning (ML) and especially deep learning (DL) is increasingly used for SLS quality control in recent time.
In this project, we investigated applications of DL to implement an in-situ quality control of the SLS process.
Cooperation partners:
High Tech Manufactorim (HTM) department, University of Applied Sciences FH Campus Vienna.
TU Vienna, Faculty for Mechanical Engineering, Prof. Andereas Otto
Digiphot – cooperative PhD study, PhD student Victor Klamert
Bachelor Works
Publications
Klamert Victor, Schmid-Kietreibera Matthias, Bublin Mugdim. “A deep learning approach for real time process monitoring and curling defect detection in selective laser sintering by infrared thermography and convolutional neural networks”, accepted for publication in 12th CIRP Conference on Photonic Technologies [LANE 2022], 4-8 September 2022, Fürth, Germany.
/
Human-Robot Collaboration

In this project, we investigate human-robot collaboration using deep reinforcement learning (DRL). Robots learn optimal sequence of operations by feedback from humans – rewards and punishments, without need for manual programming.
In the first phase of the project, we use (virtual reality) simultation environment of Unity game engine. In the second phase, we are going to use Sawyer robot for real-world deployment.
Cooperation partners:
High Tech Manufactorim (HTM) department, University of Applied Sciences FH Campus Vienna.
Bachelor Works
Supervised Learning (Bachelor thesis 2)
/
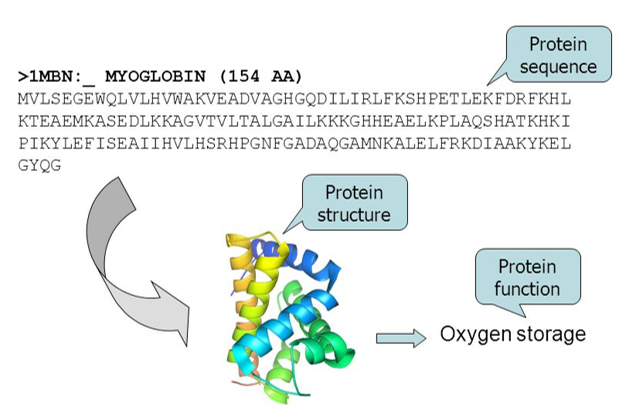
Protein Structure and Function Prediction
•Understanding immunity and autoimmunity: –The immune system enables antibodies to distinguish between foreign and self molecules e.g. autoimmune diseases are characterized by the inappropriate response to self-antigens. Understanding the mechanisms that underlie Ab-Ag recognition, therefore, is crucial for understanding immunity. –Antibody-Antigen interfaces are often considered a model system for elucidating the principles governing biomolecular recognition .
•Antibody engineering –The specificity of the antibodies molecule to its cognate antigen has been exploited for the development of a variety of immunoassays, vaccinations, and therapeutics. –Ab engineering may offer to expand the application of Abs by permitting improvements of affinity and specificity
•Antibody epitope prediction –understanding the way in which an antibody recognizes its cognate epitope is of particular interest for vaccine design and disease prevention Epitopes are used in the development of vaccines and in immunodiagnostics. Correct identification of epitopes within an antigenic protein, may open the door for the design of molecules (biologic or synthetic) that mimic potentially protective epitopes and could be used to raise specific antibodies or be used as a prophylactic or therapeutic vaccines.
In this project, we investigate applications of deep learning on protein structure and function prediction, with emphasis on collaboration with microbiologists and their experimental work.
Cooperation partner:
Assoc.-Prof. Priv.-Doz. Mag. Dr. Merima Bublin,
Medical University of Vienna
Department of Pathophysiology and Allergy Research
Bachelor Works
/
Handwritting analysis by deep learning using SensoGrip

Handwritting difficulties can have a serious negative impact on children’s academic results, daily life and overall wellbeing. Early detection of handwritting difficulties can help early intervention and an appropriate therapeutic care. We investigate handwriting capabilities by deep learning using a smart pen (SensoGrip), a pen with sensor capabilities, developed by the department of Health Assisting Engineering at FH Campus Wien.
Cooperation partners:
Health Assisting Engineering, FH Campus Wien.
Bachelor Works
/
Artificial Intelligence in Internet of Things
Using sensors to collect data from „things“ like water and electricity usage, gas and oil pipelines, streets etc. (IoT), and intelligent data processing by AI, increase efficiency, safety and reliability, and enables smart cities, smart energy, smart helth.
Master Works
Publications